A recurring deposit is a type of term deposit offered by banks / financial institutes which assist people with regular incomes to deposit a fixed amount every month into their RD account and earn interest at the rate applicable. Recurring Deposit is a product to provide a person with an opportunity to build up saving through regular monthly deposits of fixed sum over a period of time Features Period of deposit Minimum - 12 months,Maximum - 120 months. To open an account Savings Bank(SB), Recurring Deposit(RD), Time Deposit(TD), Monthly Income Scheme(MIS) SB3, SB103 (pay-in-slip) and specimen signature slip for SB and TD are required. For senior citizen accounts, separate forms are to be used. For SB account introduction is compulsory. What is silent account and how to revive it? A recurring deposit allows you to save a pre-determined amount every month with the benefit of compounding through interest income. A recurring deposit can help bring in discipline for long-term savings and even provide a loan against RD in times of financial distress.
- Recurring Deposit Formula
- Recurring Deposit Interest Rate
- Sbi Recurring Deposit Calculator
- Recurring Deposit Axis Bank
- Recurring Deposit Interest

In this article [show]
Recurring Deposit Meaning
An RD (Recurring Deposit) is a special type of term deposit offered by the banks and post office which lets people deposit a specific amount every month into their RD account and earn returns at the rates offered for FDs. It is similar to initiating an FD of a specific amount in monthly installments. This scheme matures on a specific future date along with all the deposit amounts made every month. This scheme allows individuals an opportunity to build up their savings through regular monthly deposits of a fixed amount over a fixed tenure. The minimum tenure for an RD is generally 6 months and the maximum varies from institution to institution. RDs can be funded by standing mandates which are the orders by depositors to the bank to withdraw a specific amount from their current/saving account and credit to the recurring deposit account.
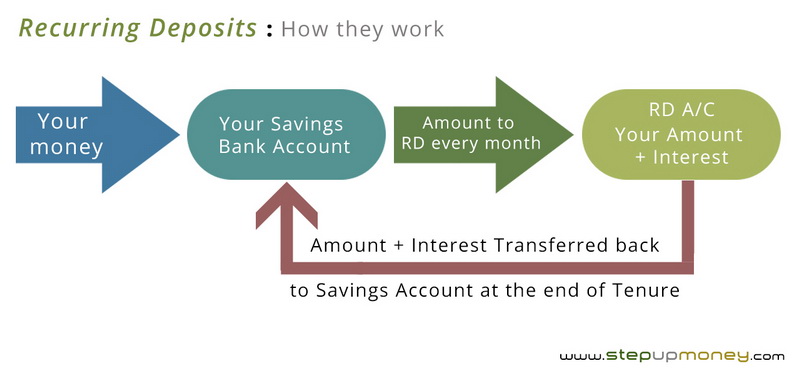
How RDs Work?
One can consider RDs as one of the simplest forms of investment. Let’s take an illustration for better understanding.
Let us assume that X wants to invest Rs 1,000 per month. He/she can either walk into any branch of a bank or post office or open an account online. If one opts to deposit Rs 1000 every month for a tenure of 12 months, then he/she will get a sum of Rs. 12,000 along with the accumulated interest at the maturity of the RD.
The depositors can plan to save for their future financial goals by using RDs. For instance, if one requires a lump-sum amount of Rs 1,00,000 after 1 year. Therefore, he/she can save around Rs. 8000 each month and make a deposit into the RD account. This way he/she will also earn interest on the amount.
WHY RD (Recurring Deposit)?
1. Higher rate of interest than savings account:
Interest rates here are identical to the interest rates offered in the fixed deposits. And generally, it is observed that RD fetches a higher return when compared to saving bank accounts.
2. Flexibility to invest on a monthly basis:
Unlike Fixed Deposits, investors can go for regular deposits. This is ideal for those who do not have a big amount of funds with them but have the capacity to save a decent amount of money regularly.
3. Guaranteed Returns:
RD is one of the safest investment options available. Since the market is not linked, a disturbance in the economy won’t affect the depositor’s returns. They will receive a profit on the rate promised to them at the time of initiating the RD. However, some of the RDs with lower-rated financial institutions & banks can be risky and therefore depositors must give attention to the credit ratings of institutions before making a deposit.
4. Short deposit tenure:
Investing in an RD gives one the option to go for a shorter duration. This leads to better liquidity and is ideal for those who want to target their short-term goals efficiently.
ELIGIBILITY
- Any Individual
- Any minor (above the age of 10 years) is eligible to initiate an RD, provided he submits the proof of name.
- Any minor (of the age 10 years or less) can initiate an RD under the guardianship of a legal or natural guardian.
- Any Company, Corporate, Govt Organisation, Proprietorship, or Commercial Organisation is eligible to open an RD account.
DOCUMENTS REQUIRED
- Identity proof: PAN/Aadhar/License
- Duly filled and signed application form of the bank
- KYC documents (if needed)
- Passport size photograph
KEY FEATURES
1. Deposit Term:
The minimum tenure starts at 6 months. One can choose a suitable tenure according to the convenience stretching up to 10 years.
2. Interest Rate:
The returns offered here are always more than the savings bank account. The interest rates are also identical to that of FDs.
3. Minimum Investment:
The minimum investment amount differs from bank to bank. One can open this account with an amount as mere as Rs. 10.
4. Withdrawal on maturity:
Withdrawal from RDs is allowed only after it attains maturity. However, if one chooses to withdraw the amount before the maturity tenure, it attracts a penalty.
5. Loan against deposit: The depositor is also offered an option to avail of a loan against the RD. Banks may allow up to 95% of the deposit amount as a loan against the deposit to be used as security/collateral.
6. Standing instructions for monthly deposits:
If one finds it inconvenient to deposit the amount periodically, banks also facilitate such payments as deductions from a linked account (current or saving) upon standing mandate or instructions.
TYPES OF RD
Apart from the regular RDs that one can invest in to earn returns and grow the corpus, RDs are also available in other types, ideal for different investors. Let’s have a look.
1. RD for senior citizens:
The scheme for senior citizens brings higher returns than regular accounts. The interest is compounded quarterly as per the applicable returns, thus facilitating senior citizens to withdraw a higher maturity corpus and meet their short-term funding needs efficiently in the absence of a regular source of income.
Generally, the additional returns offered by various institutions on the senior citizen RD scheme range between 0.25% and 0.75% p.a. above the regular rates.
2. RD for NRI/NRE:
RD schemes are one of the best investment options for Non-Resident Indians i.e. NRIs. Decent returns through investment can be generated with a small recurring deposit every month. As an NRI, one can invest in RDs either through an NRO or NRE RD account.
Recurring Deposit Formula
3. Flexi RD:
These schemes allow an individual to invest a flexible amount as per one’s convenience. In this type of deposit, while the core investment amount is pre-decided, the depositor has an option to deposit amounts in multiples of the core principal amount.
RATES ACROSS TOP BANKS AND POST OFFICE
TAXATION OF RD
Just like an FD scheme, returns earned on an RD deposit are added to the annual income of the investor. This income goes to the ‘Income from Other Sources’ head and is fully taxable as per the applicable income tax slab rate.
No tax is levied if income earned from bank or post office deposits amounts to Rs. 40,000 or less. But if it goes beyond the Rs. 40,000 limit, banks charge 10% as Tax Deducted at Source i.e. TDS.
Recurring Deposit Interest Rate
PREMATURE WITHDRAWAL OF RD
- If the depositor withdraws the amount before it matures, the rate of return will be the one applicable to the period for which the deposit has remained with the institution. Generally, for premature withdrawals in RDs, a 1% penalty will also be levied.
- However, some institutions would deduct a penalty of 1% to 2% from the applicable interest rate for the period during which the deposit remained in the bank in case of premature withdrawals.
- Generally, the minimum lock-in period for a Recurring Deposit account is 3 months. If a premature withdrawal is made before this period, the depositor would earn zero interest and only the principal amount that was deposited would be refunded to him/her by the bank.
- In addition to a penalty on interest, the depositor is not eligible for incentives offered by the bank on the RD.
Sbi Recurring Deposit Calculator
More Information:
Recurring Deposit Axis Bank
Understand the Difference Between FD and RD
RD vs SIP - Risk, Returns, Benefits, Tenure, Comparison, Which is Better Investment
Kisan Credit Card (KCC): Scheme Eligibility, Interest Rate, Loan Fee, Online Apply
Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP) Scheme - Benefits, Interest Rate, Types, Calculation
Post Office Saving Schemes: Types, Plans, Benefits, Who Should Invest
What is Fixed Deposit: Meaning, Interest Rates, Benefits, Risk, Bank fd vs Corporate fd
PM Vaya Vandana Yojana (PMVVY): Scheme Eligibility, Interest Rate, Process to Apply
Best Mid Cap Mutual Funds to Invest in India
Best Multi Cap Funds to Invest in India
Check Latest Post Office Fixed Deposit (FD) Interest Rate